The NIH Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEX) project was created to establish a sample and data resource for studies on the relationship between genetic variation and gene expression in multiple human tissues. This track hub shows tracks of analysis results from the GTEx midpoint milestone data release (V6, October 2015).
The first tracks available from this hub are summary Allele-Specific Expression (ASE), provided by the Lappalainen Lab at the New York Genome Center (as part of the GTEx Analysis Working Group. Additional analysis tracks will be added as they become available.
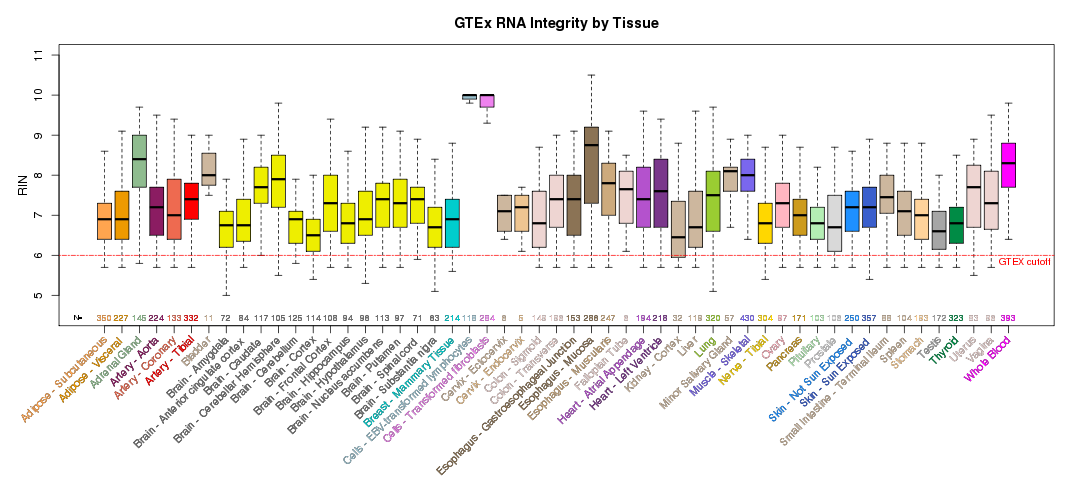
For other GTEx resources in the UCSC Genome Browser, see the GTEx Gene Expression track and the GTEx RNA-Seq Signal Hub.The scientific goal of the GTEx project required that the donors and their biospecimen present with no evidence of disease. The tissue types collected were chosen based on their clinical significance, logistical feasibility and their relevance to the scientific goal of the project and the research community. Postmortem samples were collected from non-diseased donors with ages ranging from 20 to 79. 34.4% of donors were female and 65.6% male.

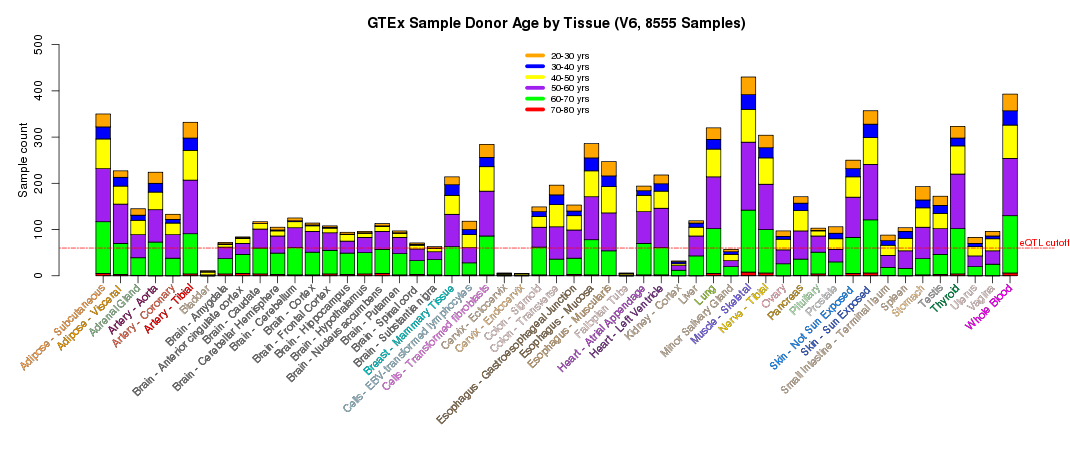
Additional summary plots of GTEx sample characteristics are available at the GTEx Portal Tissue Summary page.
Samples were collected by the GTEx Consortium. RNA-seq and genotyping were performed by the GTEx Laboratory, Data Analysis and Coordinating Center (LDACC) at the Broad Institute. Further analyses were performed by members of the GTEx Analysis Working Group (see each track for credits). The UCSC Genome Browser group post-processed the analysis files and created this track hub.
For questions about the GTEx data, contact the GTEx LDACC at the Broad Institute. For questions about individual tracks on this hub, see the contact listed on the track description. For questions about this track hub, contact the UCSC Genome Browser mailing list.
GTEx Consortium. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat Genet. 2013 Jun;45(6):580-5. PMID: 23715323; PMC: PMC4010069